Linux Kernel Debugging using VirtualBox and GDB
If you don’t want to read the whole thing, just go to the TLDR section with the precise steps on what and how to install/configure.
Debugging the operation system in real time and seeing how interrupts occurs and threads context switching is a fascinating thing I must say. While working on a PingPorts, I was curious how the OS network stack decides when to send a TCP Reset (RST) packet when nobody listens on the port (spoiler alert! See net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c file, tcp_v4_rcv function, which calls __inet_lookup_skb and branching to no_tcp_socket). Quickly looking at the TCP/IP implementation in the kernel did not give any specific results, so I decided to setup virtual machine with the latest kernel compiled in debug mode and step in gdb to observe what is happening there. Here is steps to configure VirtualBox, build the Linux kernel and finally debug using gdb.
For the sake of clarity:
Host- The actual physical computer on which a virtual machine is running.Guest- Virtual machine running on a host.
VirtualBox Setup
I’ve used Ubuntu as host and guest OS installed on VirtualBox. Make sure you’ve installed Guest Additions on guest to be able to share compiled kernel with host (using Shared Folders settings). After the guest OS is installed, let’s configure the Serial Ports in VirtualBox, so gdb on host can communicate with the guest, let’s call it /tmp/debug-pipe.
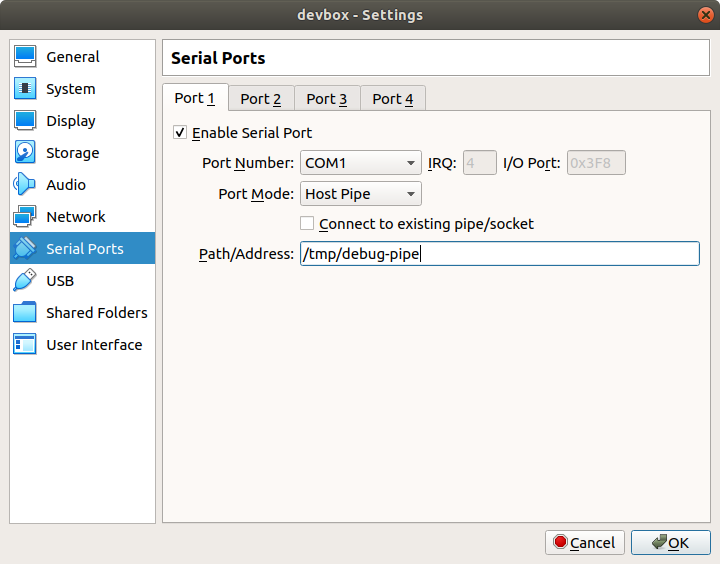 Serial port configuration in VirtualBox
Serial port configuration in VirtualBox
The next step is to install all the required software packages on guest, needed to build the kernel: sudo apt-get install git fakeroot build-essential ncurses-dev xz-utils libssl-dev bc flex libelf-dev bison
Building Linux Kernel
Go ahead and pick kernel version you want to debug, in my case it was the latest stable version on the time of writing, then, clone the source code on a guest machine: git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux-stable.git.
The configuration .config file in the kernel source root folder must be adjusted, in order to build the debug version of kernel. First, let’s copy existing kernel configuration in guest: cp /boot/config-<your_kernel_release> .config to the root folder with the kernel source code. Then, change the following configuration properties by opening .config file in text editor or running make menuconfig in a source code root folder:
- Set
CONFIG_DEBUG_INFOtoy. As the name says, this will enable including debug information into output executable modules. - Set
CONFIG_KGDBtoy. This enables built-in kernel debugger. - Comment out
CONFIG_RANDOMIZE_BASE, to disabled KASLR. This is needed asgdbwill fail to identify the correct address of symbols, when trying to set breakpoints, using function name, etc. - Set
CONFIG_GDB_SCRIPTStoy. This will create a symbolic link to thevmlinux-gdb.pygdbhelper commands and functions for kernel debugging in a source code root folder. - Set
CONFIG_KGDB_SERIAL_CONSOLEtoy. This will enable usage ofgdbover the serial console.
Now, the final step is to actually start the build process: switch to the root source code directory and run: make and then make modules, this will take some time. Then, once it has been compiled, run the installation process: sudo make modules_install, sudo make install and make scripts_gdb.
Debugger Setup
On a guest you need to enable debugging support during the boot process by editing the boot settings file: /etc/default/grub. Just append the following line:GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="console=tty0 nokaslr kgdboc=kbd,ttyS0,115200" to the end of the file and reboot the guestto use kgdb over serial console.
Now, the next step is to convert the socket created by VirtualBox (/tmp/debug-pipe) using socat tool to PTY using the following command: socat -d -d -d -d /tmp/debug-pipe PTY,link=/tmp/debug-pipe-pty.
OK, now the PTY is ready on the /tmp/debug-pipe-pty and the final step is to start gdb on a host and attach it to the guest machine.
But first, let’s share the guest kernel source code folder with the host machine, so gdb can load the vmlinux file from this folder.
After the kernel source code folder is available to host machine, run the following command in kernel source code root folder on a host: gdb vmlinux -ex "target remote /tmp/debug-pipe-pty" and immediately run the echo g > /proc/sysrq-trigger on guest machine to debug break in gdb on a host machine.
If everything works fine, there must be the following output from gdb:
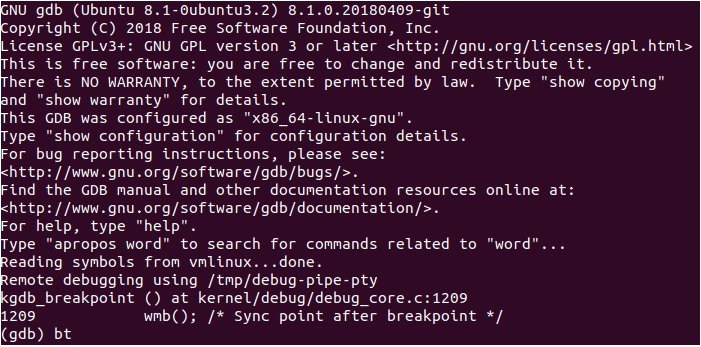 GDB on host system connected to guest
GDB on host system connected to guest
TLDR
- VirtualBox Setup:
- Install Ubuntu on VirtualBox.
- Install Guest Additions.
- Install required packages:
sudo apt-get install git fakeroot build-essential ncurses-dev xz-utils libssl-dev bc flex libelf-dev bison. - Add serial port:
/tmp/debug-pipein Serial Ports settings.
- Building Linux Kernel:
-
git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux-stable.giton theguestmachine. - Copy current kernel config file on
guestto kernel source code root folder:cp /boot/config-<your_kernel_release> .config. - Edit
.configfile in kernel source code root folder:- Set
CONFIG_DEBUG_INFOtoy. - Set
CONFIG_KGDBtoy. - Comment out
CONFIG_RANDOMIZE_BASE. - Set
CONFIG_GDB_SCRIPTStoy. - Set
CONFIG_KGDB_SERIAL_CONSOLEtoy.
- Set
- Run
makeand thenmake modulesin the kernel source code root folder. - After compilation is finished, run:
sudo make modules_install,sudo make installandmake scripts_gdb.
-
- Debugger Setup:
- Append
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="console=tty0 nokaslr kgdboc=kbd,ttyS0,115200"to/etc/default/grubon theguestmachine and reboot. - Run:
socat -d -d -d -d /tmp/debug-pipe PTY,link=/tmp/debug-pipe-ptyonhostmachine. - Share the Linux kernel source code folder from
guesttohostmachine. - Run:
gdb vmlinux -ex "target remote /tmp/debug-pipe-pty"on thehostmachine in the kernel source code folder. - Run
echo g > /proc/sysrq-triggeron theguestmachine.
- Append